9.3 KiB
9.3 KiB
| title | date | author | categories | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeoTools 矢量网格(Vector Grid) | 2023-12-20 | ac |
|
|
GeoTools 矢量网格(Vector Grid)
1.简介
GeoTools 的矢量网格化操作是
GeoTools矢量网格类使得创建由多边形或线元素组成的矢量网格(也称为网格)变得容易,其中每一个都表示为SimpleFeature。可以使用grids或Lines实用程序类轻松生成简单的网格,而当需要对网格布局和属性进行更多控制时,可以使用较低级别的类。
网格是在内存中构建的,整个网格一次构建。
2.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-grid</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
3. Polygon grids
Grids实用类提供了创建矩形或六边形元素网格的方法。
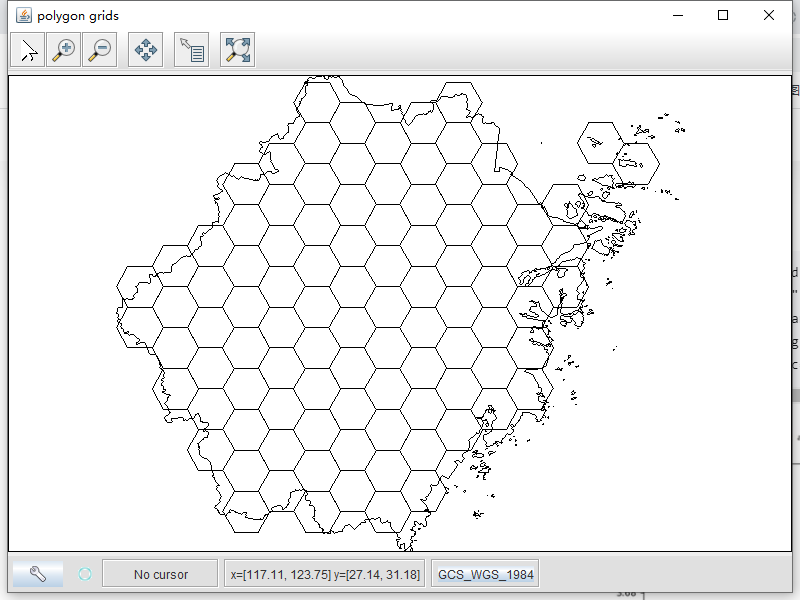
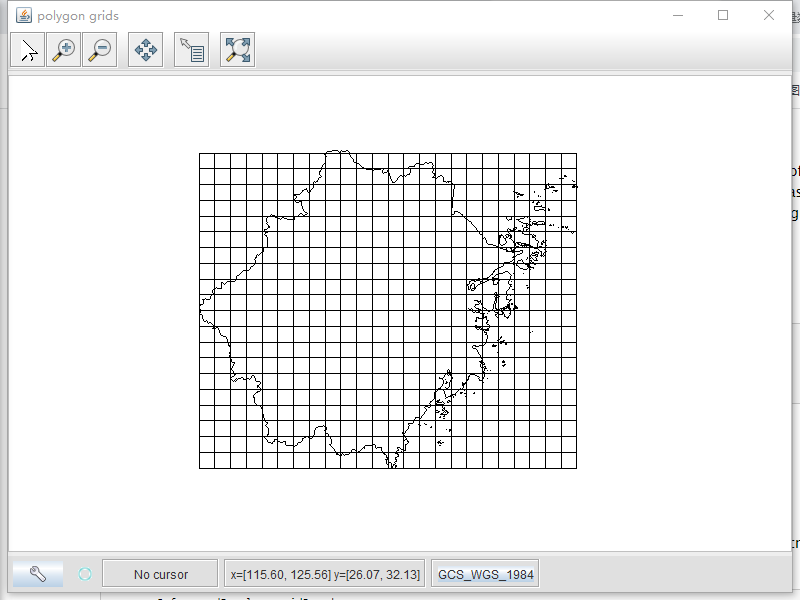
创建基本网格的最简单方法是使用Grids实用程序类中的静态方法。下面的例子创建了一个经纬度网格,其宽度为10度,用于显示在浙江地图上:
public class Le08PolygonGrids {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\demo\\tutorial\\data\\china\\zhejiang.shp";
Le08PolygonGrids.readShpFile(path);
}
public static void readShpFile(String shpPath) {
File shpFile = new File(shpPath);
try {
ShapefileDataStore shapefileDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(shpFile.toURI().toURL());
// 设置编码,防止属性的中文字符出现乱码
shapefileDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
// 这个typeNamae不传递,默认是文件名称
FeatureSource featuresource = shapefileDataStore.getFeatureSource(shapefileDataStore.getTypeNames()[0]);
// 读取bbox
ReferencedEnvelope bbox =featuresource.getBounds();
// 创建grids,0.2度为间隔
SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createSquareGrid(bbox, 0.2);
// Create a map content and add our shapefile to it
MapContent map = new MapContent();
map.setTitle("polygon grids");
// 添加shp到map中
Style style = SLD.createSimpleStyle(featuresource.getSchema());
Layer layer = new FeatureLayer(featuresource, style);
map.addLayer(layer);
Style styleBox = SLD.createSimpleStyle(grid.getSchema());
Layer layerBox = new FeatureLayer(grid, styleBox);
map.addLayer(layerBox);
// Now display the map
JMapFrame.showMap(map);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("读取完成!");
}
}
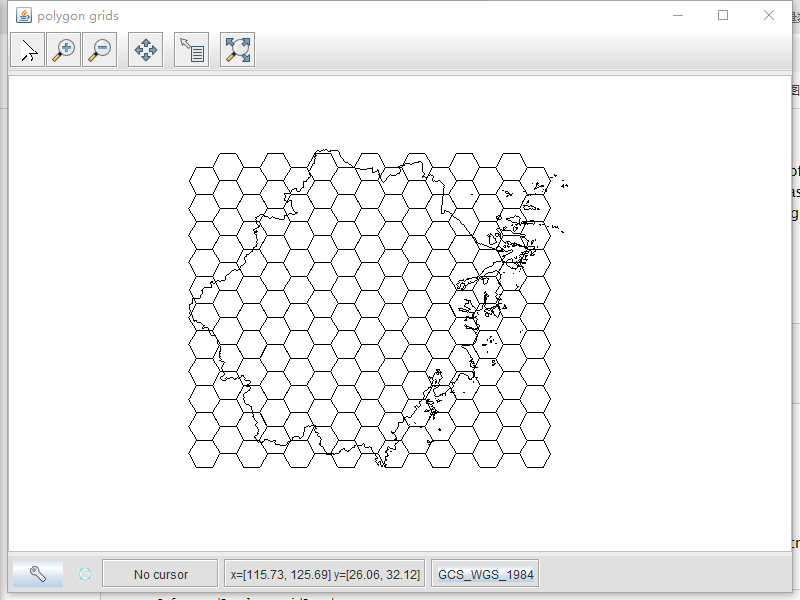
创建的网格由SimpleFeatures组成,每个SimpleFeatures都有一个最小多边形,即一个由四个角顶点表示的多边形。
选择性创建
新建一个网格生成类,继承GridFeatureBuilder,重写getCreateFeature方法来过滤与原数据要素不重叠得网格。
package learning.tools;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import org.geotools.api.data.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import org.geotools.api.filter.Filter;
import org.geotools.api.filter.FilterFactory;
import org.geotools.factory.CommonFactoryFinder;
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.JTSFactoryFinder;
import org.geotools.grid.GridElement;
import org.geotools.grid.GridFeatureBuilder;
import org.geotools.grid.PolygonElement;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Coordinate;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
public class IntersectionBuilder extends GridFeatureBuilder {
final FilterFactory ff2 = CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory();
final GeometryFactory gf = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
final SimpleFeatureSource source;
int id = 0;
public IntersectionBuilder(SimpleFeatureType type, SimpleFeatureSource source) {
super(type);
this.source = source;
}
public void setAttributes(GridElement el, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
attributes.put("id", ++id);
}
@Override
public boolean getCreateFeature(GridElement el) {
Coordinate c = ((PolygonElement) el).getCenter();
Geometry p = gf.createPoint(c);
Filter filter = ff2.intersects(ff2.property("the_geom"), ff2.literal(p));
boolean result = false;
try {
result = !source.getFeatures(filter).isEmpty();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return result;
}
}
package learning;
import learning.tools.IntersectionBuilder;
import org.geotools.api.data.FeatureSource;
import org.geotools.api.data.Query;
import org.geotools.api.data.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import org.geotools.api.feature.type.AttributeDescriptor;
import org.geotools.api.feature.type.GeometryType;
import org.geotools.api.geometry.BoundingBox;
import org.geotools.api.referencing.crs.CoordinateReferenceSystem;
import org.geotools.api.style.Style;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureCollection;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder;
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.ReferencedEnvelope;
import org.geotools.grid.GridElement;
import org.geotools.grid.GridFeatureBuilder;
import org.geotools.grid.Grids;
import org.geotools.grid.PolygonElement;
import org.geotools.map.FeatureLayer;
import org.geotools.map.Layer;
import org.geotools.map.MapContent;
import org.geotools.referencing.crs.DefaultGeographicCRS;
import org.geotools.styling.SLD;
import org.geotools.swing.JMapFrame;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Polygon;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author ac
* @date 2023/12/20 13:54
*/
public class Le08PolygonGrids {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\demo\\tutorial\\data\\china\\zhejiang.shp";
Le08PolygonGrids.readShpFile(path);
}
public static void readShpFile(String shpPath) {
File shpFile = new File(shpPath);
try {
ShapefileDataStore shapefileDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(shpFile.toURI().toURL());
// 设置编码,防止属性的中文字符出现乱码
shapefileDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
// 这个typeNamae不传递,默认是文件名称
FeatureSource featuresource = shapefileDataStore.getFeatureSource(shapefileDataStore.getTypeNames()[0]);
// 读取bbox
ReferencedEnvelope bbox =featuresource.getBounds();
Double sideLen = 0.2;
// 创建网格
// 新建一份面要素shp,名叫grid,有两个字段id,the_geom
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tb = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
tb.setName("grid");
tb.add(
GridFeatureBuilder.DEFAULT_GEOMETRY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,
Polygon.class,
bbox.getCoordinateReferenceSystem());
tb.add("id", Integer.class);
SimpleFeatureType TYPE = tb.buildFeatureType();
// Build the grid the custom feature builder class
GridFeatureBuilder builder = new IntersectionBuilder(TYPE, (SimpleFeatureSource)featuresource);
SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createHexagonalGrid(bbox, sideLen, -1, builder);
// Create a map content and add our shapefile to it
MapContent map = new MapContent();
map.setTitle("polygon grids");
// 添加shp到map中
Style style = SLD.createSimpleStyle(featuresource.getSchema());
Layer layer = new FeatureLayer(featuresource, style);
map.addLayer(layer);
Style styleBox = SLD.createSimpleStyle(grid.getSchema());
Layer layerBox = new FeatureLayer(grid, styleBox);
map.addLayer(layerBox);
// Now display the map
JMapFrame.showMap(map);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("读取完成!");
}
}
4.属性渲染
到目前为止,没有一个示例需要为矢量网格指定 feature type特征类型。相反,我们用两个属性创建了一个默认的 feature type特性类型:
- ‘element’ (the Polygon instance)
- ‘id’ (a sequential integer ID value.
当然,您也可以提供自己的特性类型,以便将其他属性与网格元素关联起来。要做到这一点,你需要重写GridFeatureBuilder类的setAttributes方法。下面的例子创建了一个带有' color '属性的特性类型。然后根据网格中每个六边形元素的位置设置颜色值: