12 KiB
12 KiB
| title | date | author | categries | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeoTools-创建要素Feature | 2023-11-19 | ac |
|
|
GeoTools-创建要素
csv2shp,通过csv转点shp文件,学习:
- 如何创建
FeatureType、FeatureCollection和Features;- 通过
GeometryFactory构建Points点集;- 输出shp文件;
- 设置投影。
1.数据准备
下载一份csv文件 ,内容格式如下:
LAT, LON, CITY, NUMBER
46.066667, 11.116667, Trento, 140
44.9441, -93.0852, St Paul, 125
13.752222, 100.493889, Bangkok, 150
45.420833, -75.69, Ottawa, 200
44.9801, -93.251867, Minneapolis, 350
46.519833, 6.6335, Lausanne, 560
48.428611, -123.365556, Victoria, 721
-33.925278, 18.423889, Cape Town, 550
-33.859972, 151.211111, Sydney, 436
41.383333, 2.183333, Barcelona, 914
39.739167, -104.984722, Denver, 869
52.95, -1.133333, Nottingham, 800
45.52, -122.681944, Portland, 840
37.5667,129.681944,Seoul,473
50.733992,7.099814,Bonn,700,2016
2.添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-shapefile</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-epsg-hsql</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>osgeo</id>
<name>OSGeo Release Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/release/</url>
<snapshots><enabled>false</enabled></snapshots>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled></releases>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>osgeo-snapshot</id>
<name>OSGeo Snapshot Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/snapshot/</url>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled></snapshots>
<releases><enabled>false</enabled></releases>
</repository>
</repositories>
3. 示例
package learning;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import org.geotools.data.DataUtilities;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStoreFactory;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureBuilder;
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.JTSFactoryFinder;
import org.geotools.swing.data.JFileDataStoreChooser;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Coordinate;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author ac
* @date 2023/11/20 15:44
*/
public class Csv2Shape {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Set cross-platform look & feel for compatability
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName());
File file = JFileDataStoreChooser.showOpenFile("csv", null);
if (file == null) {
return;
}
/*
* We use the DataUtilities class to create a FeatureType that will describe the data in our
* shapefile.
*
* See also the createFeatureType method below for another, more flexible approach.
*
* 通过 DataUtilities 创建 FeatureType ,类似定义shp文件的名称、几何类型、属性字段、空间参考等信息。
* createType (String typeName, String typeSpec)
* typeName:要素名称
* typeSpec:是"name:Type,name2:Type2,..."格式的字符串,用于定义要素的属性字段,其中Type的类型有:
* Interger(int、Interger)
* Double(Double, double)
* String("",String,string)
* Geometry(Point,LineString,Polygon,MultiLineString,MultiPolygon,MultiPoint,GeometryCollection)
* 还可以是 UUID、Date或是Java的类的全名(含包名)
* 示例:
* name:"",age:0,geom:Geometry,centroid:Point,url:java.io.URL"
* id:String,polygonProperty:Polygon:srid=32615
*/
final SimpleFeatureType TYPE =
DataUtilities.createType(
"Location",
"the_geom:Point:srid=4326,"
+ // <- the geometry attribute: Point type
"name:String,"
+ // <- a String attribute
"number:Integer" // a number attribute
);
System.out.println("TYPE:" + TYPE);
/*
* A list to collect features as we create them.
*/
List<SimpleFeature> features = new ArrayList<>();
/*
* GeometryFactory will be used to create the geometry attribute of each feature,
* using a Point object for the location.
* 创建几何工厂实例,要素构建者实例
* 通过缓冲流一行行读取,解析数据,构建Point实例
*/
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(TYPE);
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) {
/* First line of the data file is the header */
String line = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Header: " + line);
for (line = reader.readLine(); line != null; line = reader.readLine()) {
if (line.trim().length() > 0) { // skip blank lines
String[] tokens = line.split("\\,");
double latitude = Double.parseDouble(tokens[0]);
double longitude = Double.parseDouble(tokens[1]);
String name = tokens[2].trim();
int number = Integer.parseInt(tokens[3].trim());
/* Longitude (= x coord) first ! */
// 创建几何实例geometry - point
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint(new Coordinate(longitude, latitude));
// 创建要素实例feature
// feature
// ↙ ↘
// geometry properties
featureBuilder.add(point);
featureBuilder.add(name);
featureBuilder.add(number);
//buildFeature(id)创建一个要素,ID可以是null,当ID为null时会由builder内部生成
SimpleFeature feature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null);
features.add(feature);
}
}
}
/*
* Get an output file name and create the new shapefile
*
* 设置输出路径
*/
File newFile = getNewShapeFile(file);
// 创建shapefile类型的数据存储工厂实例
ShapefileDataStoreFactory dataStoreFactory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("url", newFile.toURI().toURL());
params.put("create spatial index", Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建一个空的数据存储
ShapefileDataStore newDataStore = (ShapefileDataStore) dataStoreFactory.createNewDataStore(params);
/*
* TYPE is used as a template to describe the file contents
* 添加类型描述
*/
newDataStore.createSchema(TYPE);
/*
* Write the features to the shapefile
* 创建“create”类型的事务,输出shapefile文件
*/
Transaction transaction = new DefaultTransaction("create");
String typeName = newDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = newDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
SimpleFeatureType SHAPE_TYPE = featureSource.getSchema();
/*
* The Shapefile format has a couple limitations:
* - "the_geom" is always first, and used for the geometry attribute name
* - "the_geom" must be of type Point, MultiPoint, MuiltiLineString, MultiPolygon
* - Attribute names are limited in length
* - Not all data types are supported (example Timestamp represented as Date)
*
* Each data store has different limitations so check the resulting SimpleFeatureType.
*/
System.out.println("SHAPE:" + SHAPE_TYPE);
if (featureSource instanceof SimpleFeatureStore) {
SimpleFeatureStore featureStore = (SimpleFeatureStore) featureSource;
/*
* SimpleFeatureStore has a method to add features from a
* SimpleFeatureCollection object, so we use the ListFeatureCollection
* class to wrap our list of features.
*/
SimpleFeatureCollection collection = new ListFeatureCollection(TYPE, features);
featureStore.setTransaction(transaction);
try {
featureStore.addFeatures(collection);
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception problem) {
problem.printStackTrace();
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
transaction.close();
}
System.exit(0); // success!
} else {
System.out.println(typeName + " does not support read/write access");
System.exit(1);
}
}
/**
* Prompt the user for the name and path to use for the output shapefile
* 弹窗让用户选择新生成的shp文件的保存位置
*
* @param csvFile the input csv file used to create a default shapefile name
* @return name and path for the shapefile as a new File object
*/
private static File getNewShapeFile(File csvFile) {
String path = csvFile.getAbsolutePath();
String newPath = path.substring(0, path.length() - 4) + ".shp";
JFileDataStoreChooser chooser = new JFileDataStoreChooser("shp");
chooser.setDialogTitle("Save shapefile");
chooser.setSelectedFile(new File(newPath));
int returnVal = chooser.showSaveDialog(null);
if (returnVal != JFileDataStoreChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
// the user cancelled the dialog
System.exit(0);
}
File newFile = chooser.getSelectedFile();
if (newFile.equals(csvFile)) {
System.out.println("Error: cannot replace " + csvFile);
System.exit(0);
}
return newFile;
}
}
4. 归纳
下面是Java中的一些对象与Geospatial中的类的对应关系:
| Java | Geospatial |
|---|---|
Object |
Feature |
Class |
FeatureType |
Field |
Attribute |
Method |
Operation |
- 先创建
SimpleFeatureType,就像新建了一个shpefile文件一样,定义了shp 文件名和属性字段。 - 通过缓冲流解析文件中的坐标和属性信息,使用
GeometryFactory几何工厂实例创建几何实例,再通过featureBuilder构建要素实例feature
数据存储
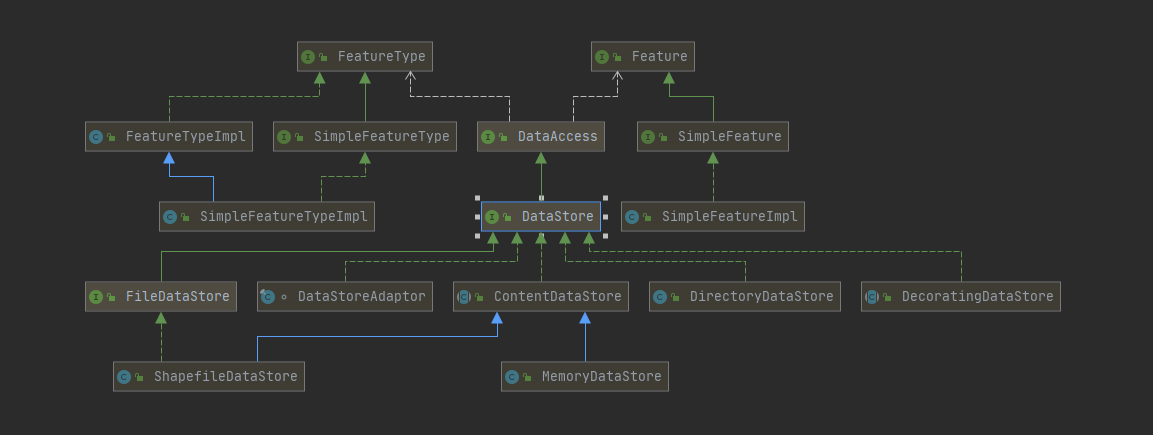
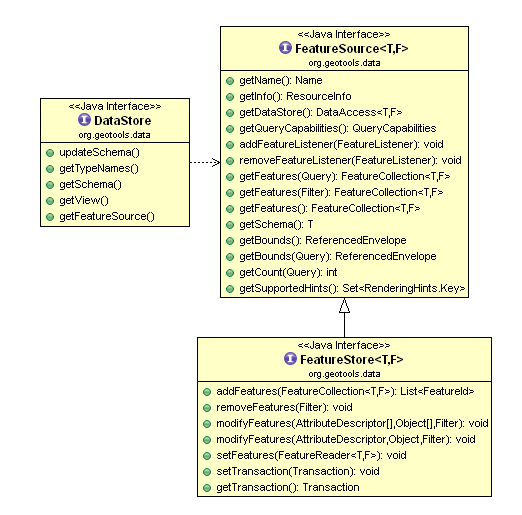
DataStore代表一份要素数据的物理的源,如shpaefile文件、数据库(要素会转为SimpleFeature实例对象)。
要素存储
FeatureSource 提供更易于操作feature data要素数据的API,当使用数据源(如shapefile或数据库表)时,您将首先创建一个DataStore对象来连接到物理源,然后检索一个FeatureSource来处理要素数据。
FeatureSource是用来【读取】要素的类似View,而其子类FeatureStore是用来【读写】要素的类似于Table
File file = ...
FileDataStore store = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(file);
FeatureSource featureSource = store.getFeatureSource();
事务
Transaction 是有要素存储FeatureStore的事务控制器。
在这个接口的帮助下,可以安全地修改Shapefiles、数据库等。事务还可以在使用锁定Feature要素时提供授权。
所有操作都被认为是在一个事务中进行的。Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT用于表示自动提交事务模式。
参考文章
[1] Feature Tutorial https://docs.geotools.org/latest/userguide/tutorial/feature/csv2shp.html